Supply chain finance solutions tailored to suit your business
Managing working capital programs involves processing vast amounts of data, but outdated technology and manual processes have made the effort slow and inefficient. The FIS® Supply Chain Finance (formerly Demica) platform helps reduce complexity and increase flexibility for banks and corporations, as its technology enables them to deliver and access the full spectrum of supply chain finance solutions.
Configurable for any working capital structure
The FIS Supply Chain Finance Platform enables you to set up, implement and manage the full range of working capital solutions in a single place. Leverage the platform to structure trade receivables solutions, customize supplier onboarding in payables finance programs and automate reporting in complex securitizations – all while being guided and supported by our expert advisory teams.
See details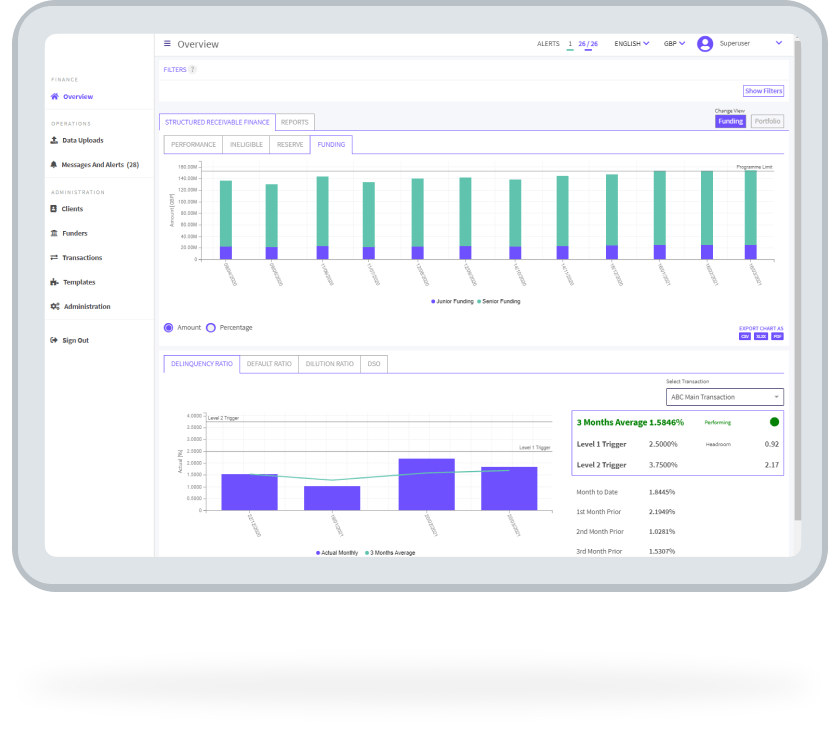
Bridging risk and financial management
Meeting funder expectations for risk management requires detailed reporting, transparency and integration, making them crucial for banks offering structured solutions. Read articleLeverage expertise, ensure compliance
Partnering with third-party technology providers, banks can use their expertise to offer superior products while maintaining security and compliance standards. Read articleBrowse more articles and videos relevant to your business
Go to Fintech InsightsLet’s keep the conversation going
Learn more about how FIS empowers banks and corporates in simplifying, automating and scaling their working capital solutions.
Connect with an expert to get all your questions answered.
Find out how to customize the platform for your operations.
Reach out for pricing details that align with your needs.
View detailed specifications for Supply Chain Finance.
Specs
Supply Chain Finance
Simplified transaction management and reporting powered by a dynamic platform
Expert delivery from initial program setup to platform integration and deal implementation
One powerful platform, multiple products
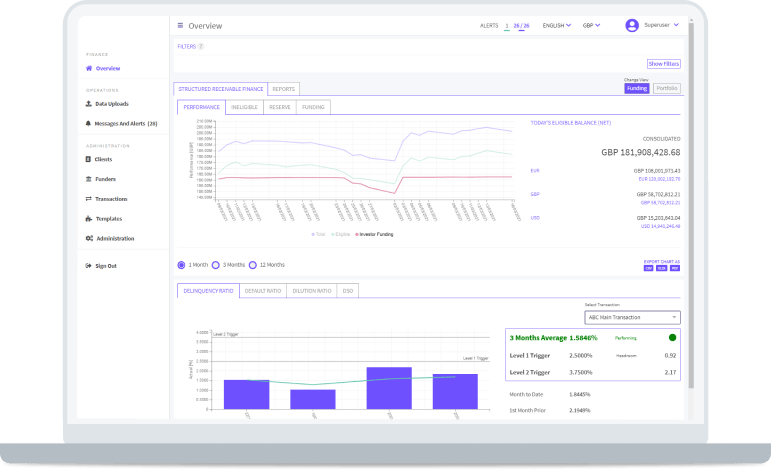
With our web-based platform, teams can collaborate on transactions with user-friendly structuring tools for managing payables and receivables while our onboarding tool connects sellers, buyers and banks directly to the platform. Granular reporting provides real-time insights into receivables performance, whether you choose the FIS®-branded platform or a while-labeled version.
Resources
Receivables Finance product sheet
A cloud-native solution designed to help businesses unlock cash trapped in outstanding payments and reduce the cost of funds.
Trade Receivables Securitization product sheet
A solution to tap into capital markets to sell a diversified pool of your company’s receivables, release capital and improve financial metrics.
FAQ
What is supply chain finance?
What is payables finance?
How it works:
- The supplier sends an invoice to the buyer.
- The buyer confirms that they have received the invoice from the supplier.
- Payment terms are agreed between the buyer and the supplier.
- Early payments terms are sent to the funder.
- The funder pays the supplier their invoice amount with the discount applied.
- The buyer pays the funder the agreed amount at invoice maturity.
What is trade finance?
The objective of trade finance is to minimize the risks associated with cross-border transactions and ensure the smooth flow of goods and services between buyers and sellers in different countries. It provides the necessary funding and financial tools to bridge the gap between the time when goods are shipped and when payment is received, reducing the cash flow constraints faced by businesses engaged in international trade.
What is trade receivables finance?
See more details
What is trade receivables securitization?
See more details
What is the difference between factoring and securitization?
Securitization uses a special purpose vehicle (SPV) to purchase their pool of receivables. An SPV is an entity created by the selling company and is independent of the company’s balance sheet. The SPV sells the financial notes of these receivables to the funder in exchange the finance, which is passed back through the SPV to the corporate. This is an off-balance sheet treatment because the SPV is the now the owner of the receivables.
Similarities:
- They are receivables finance solutions.
- They allow companies to remove their outstanding receivables from their balance sheets.
- The risk associated with the lines of credit are based on the payment history of the company’s book of receivables.
- Funds in a securitization don’t pass directly from funder to the company.
- For a securitization to work, a company needs a large book of receivables to pass through the SPV due to the complexities of the structure.
- In a securitization, the risk sits with the SPV rather than the company.
What is distributor finance?
How it works:
- The distributor raises a purchase order (PO) with the manufacturer.
- A PO is submitted for approval based on limits.
- For an approved PO, the manufacturer dispatches the goods and sends an invoice.
- The invoice is submitted to the platform and checked against funding criteria.
- Where manufacturer early payment is required, eligible invoices are submitted to funders.
- The funder provides payment for the full invoice to the manufacturer.
- If no extension is required, the distributor pays the funder the full amount at maturity.
- Maturity date extension is requested by the distributor, approved, and all parties are notified.
- The distributor pays the funder the full invoice amount at extended maturity.
What is dynamic discounting?
How it works:
- An invoice is issued to the buyer from the supplier.
- The buyer approves the invoice.
- The buyer decides when to early pay the invoice.
- A discount is calculated and applied to the invoice value based on the commercial terms agreed.
- The buyer pays the invoice early.
What is working capital management?
The objective is to maintain a balance between liquidity and profitability by having enough working capital to cover obligations and daily expenses while minimizing costs and excessive investments in current assets.
Let’s keep our conversation going
Learn more about how FIS empowers banks and corporates in simplifying, automating and scaling their working capital solutions.
Connect with an expert to get all your questions answered.
Find out how to customize the platform for your operations.
Reach out for pricing details that align with your needs.
Get a brief overview of Supply Chain Finance.



